Chapter 5 - Project Charter¶
Part 4¶
Summary¶
To summarise the keywords of that chapter, here is a quick overview:
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Deming cycle | Quality improvement and problem solving-method Plan - Do - Check - Act |
| Magic triangle | Visualises the prioritised three main objectives quality, time and cost |
| Operationalising | The operationalising of an objective means making it measurable and therefore verifiable Establish measures for deadlines and cost adherence Use performance indicators and characteristic curves for performance objectives |
| Target relationships | Characterises the relationship between project goals/objectives One differentiates between competing and complementary relationships |
| Special characteristics of contracts in projects | Acceptance Warranty Exclusion of liability Limitation of defect claims |
| Customer's rights in performance impairment | Contractual penalty Retaining lien Supplementary performance Self-execution Price reduction and cancellation of contract Damages Termination for cause |
| Contractor's rights in performance impairment | Retaining lien Default interest Cancellation of the contract Damages Termination for cause |
| Contract administrator | Should have interdisciplinary knowledge |
| Contracts of sale | Obligation to deliver the purchased item |
| Contracts for service | Obligation to perform the service |
| Contracts for work and service | Obligation to produce the item |
| Competing goals | The relationship of competitive relationships (= conflicts of interest) often exist The more fully one objective is attained, the less completely the other is |
| Complementary goals | The relationship of complementary goals is unproblematic since the more fully one objective is attained, the more completely the second objective is also achieved |
| Quality | Since it relates to all characteristics/features of a product, quality means the product itself Quality can also describe the conformity of the performance delivered to the customer's specifications |
Let's practice¶
Now it's your turn.
You remember what your friend told you about the wedding? No? Maybe you look that up again and work out the project charter for this one!
Solution
Here you can see the sample solution:
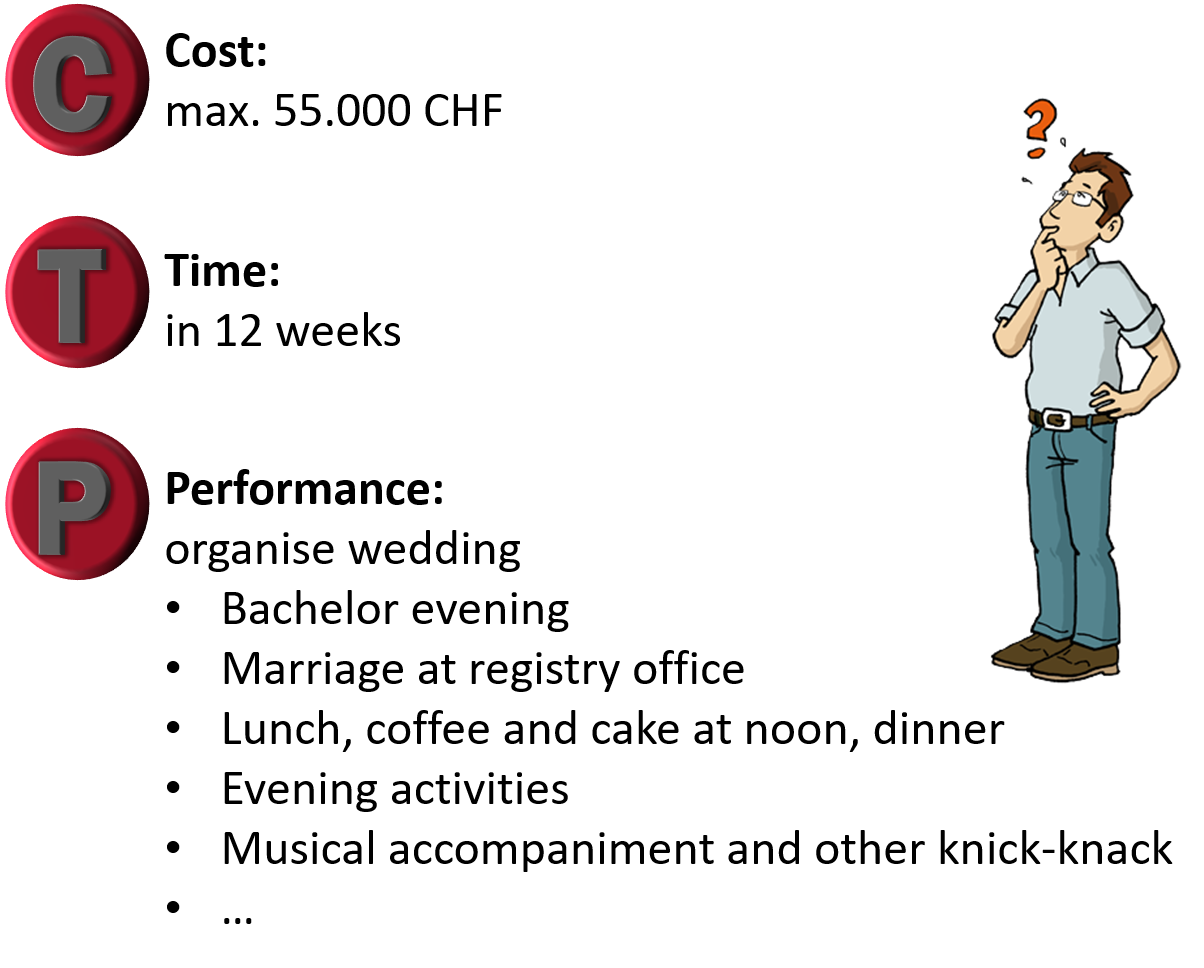
Let's prioritise the objectives:
Your friend asked you not to exceed his budget, so cost is clearly top priority.
Then he said, he wanted the best day in his life. So, the quality would be on second place.
Ultimately, the time has the lowest priority.
Test yourself!¶
Now it is time to check your knowledge.
Answer the following questions for yourself. Please take your time and think carefully about what you would answer before revealing the solution.
Where are the quality objectives for the project generally documented?
In the statement of work or the supplier (performance) specification.
Why are project objectives linked to business objectives?
To identify the interdependencies between different projects and also the strategy underlying the individual projects.
What basic procedures for problem solving can be applied?
Sequential phase models
In each project phase, a problem solving sub-process takes place. When one phase ends, the next one starts.
Problem solving cycle
The iterative process of the Deming cycle: Plan - Implement (Do) - Check - Control (Act)
→ The starting point of each cycle is the result of the previous cycle.
Form-based systems
Cause-and-effect diagram (problem broken down to identify possible causes)
It compiles stakeholder information requirements in a list and specifies report type, frequency, summarisation and distribution. It ensures that the information recipients are provided with the correct quantity of information
→ enough to give them an idea of what is going on but in summarised format to ensure that they can retain an overview.
When is a contract considered to be accepted or to have become effective?
- When a written or verbal offer is made by one party and unconditionally accepted (i.e. without reservation) by the other party
- Verbal agreements have legal force, but they are not recommended because it is difficult to prove what has been agreed
- When it has been signed by all parties or their representatives
What basic procedures for problem solving can be applied?
- Law governing contracts of sale (obligation to deliver the purchased item)
- Law governing contracts for services (obligation to perform the services)
- Law governing contracts for work and services (obligation to produce the item)
When is a contract invalid in a country with freedom of contract?
In countries with freedom of contract (contractual autonomy) all contractual provisions are admissible and valid, subject to limits defined by constitutions.
The parties to the contract must observe effective statutory provisions and the principles of common decency. Contracts that breach these laws and principles are invalid.
What things do you have to check in international contracts?
It is necessary to establish on a case-by-case basis whether the conclusion and content of contracts are subject to any national approval procedures.
What special features characterise project contracts?
- Acceptance
- Warranty
- Exclusion of liability
- Limitation of defect claims
What rights has a customer in the event of performance impairment?
- Contractual penalty
- Refusal of performance until counter-performance is affected (= retaining lien)
- Supplementary performance (formerly: rectification of defects - takes precedence over other defect claims)
- Self-execution (formerly: execution by substitution)
- Price reduction and cancellation of the contract
- Damages (if the contractor is at fault)
- Termination for cause
What rights has a contractor in the event of performance impairment?
- Refusal of performance until counter-performance is affected (= retaining lien)
- Default interest
- Cancellation of the contract
- Damages (if the customer is at fault)
- Termination for cause
What tasks and process steps are involved in contract administration and what are the primary contract administration tools?
Contract administration is the part of project management concerned with the coordination of contract design, conclusion, execution with a view to attaining the project objectives and modification.
Tools used for contract administration are the various forms of available documentation (contracts, change logs, construction site reports, delivery notes, forms and checklists...).
What skills/knowledge should a contract administrator have?
Contract administrators should have interdisciplinary knowledge. Engineers with commercial knowledge or vice-versa, plus a basic understanding of the law.