Chapter 12 - Process and Time Schedule¶
Part 3¶
Summary¶
To summarise the keywords of that chapter, here is a quick overview:
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Process schedule | = Project network diagram A schedule that divides a complex process into sub-processes (activities) Generally includes |
| Total float (TF) | Available time, derived from the network plan, by which an activity can be extended or delayed without any impact on the project finish date |
| Free float (FF) | The amount of float available when all predecessor activities are scheduled for their earliest deadlines |
| Project control function | The broader concept of project control not only includes time scheduling, but also the scheduling of costs, quality and resources Explanations of variance analyses also apply for resources, costs and quality |
| Event | Element representing the occurrence of a specific status Occurs at a specific point in time (time of occurrence) or is attained at a specific point in time Does not have any duration Events of special significance during the project are called key events or milestones. |
| Standard sequence (SdS) | = Finish-to-start relationship Exists between the finish of the predecessor activity and the start of the successor activity |
| Start sequence (StS) | = Start-to-start relationship Exists between the start of the predecessor activity and the start of the successor activity |
| Finish sequence (FS) | = Finish-to-finish relationship Exists between the finish of the predecessor activity and the finish of the successor activity |
| Jump sequence (JS) | = Start-to-finish relationship Exists between the start of the predecessor activity and the finish of the successor activity |
| Minimum and maximum lags | In practice often necessary to adhere to a minimum or maximum lag between activities |
Let's practice - transfer project¶
Now it's your turn to calculate a network diagram.
The network diagram of the wedding would be too extensive to calculate, which is why the sample solution can be found right here. For practice, you will find two exercise plans with model solutions here.
Your first task:
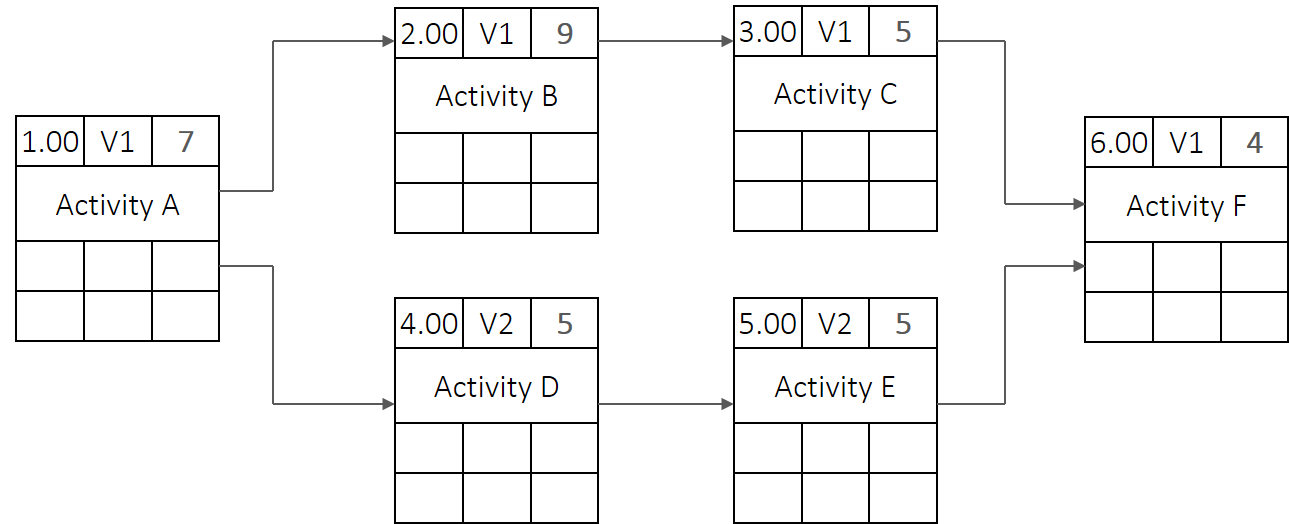
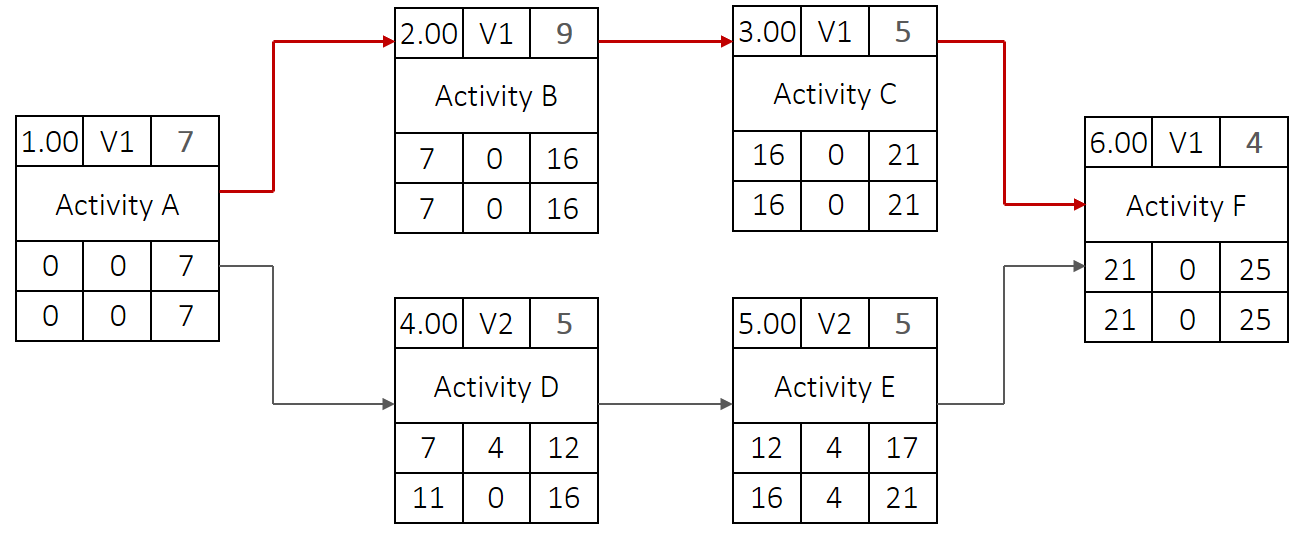
Solution for the first task
How to solve:
Filled out network diagram:
Your first task:
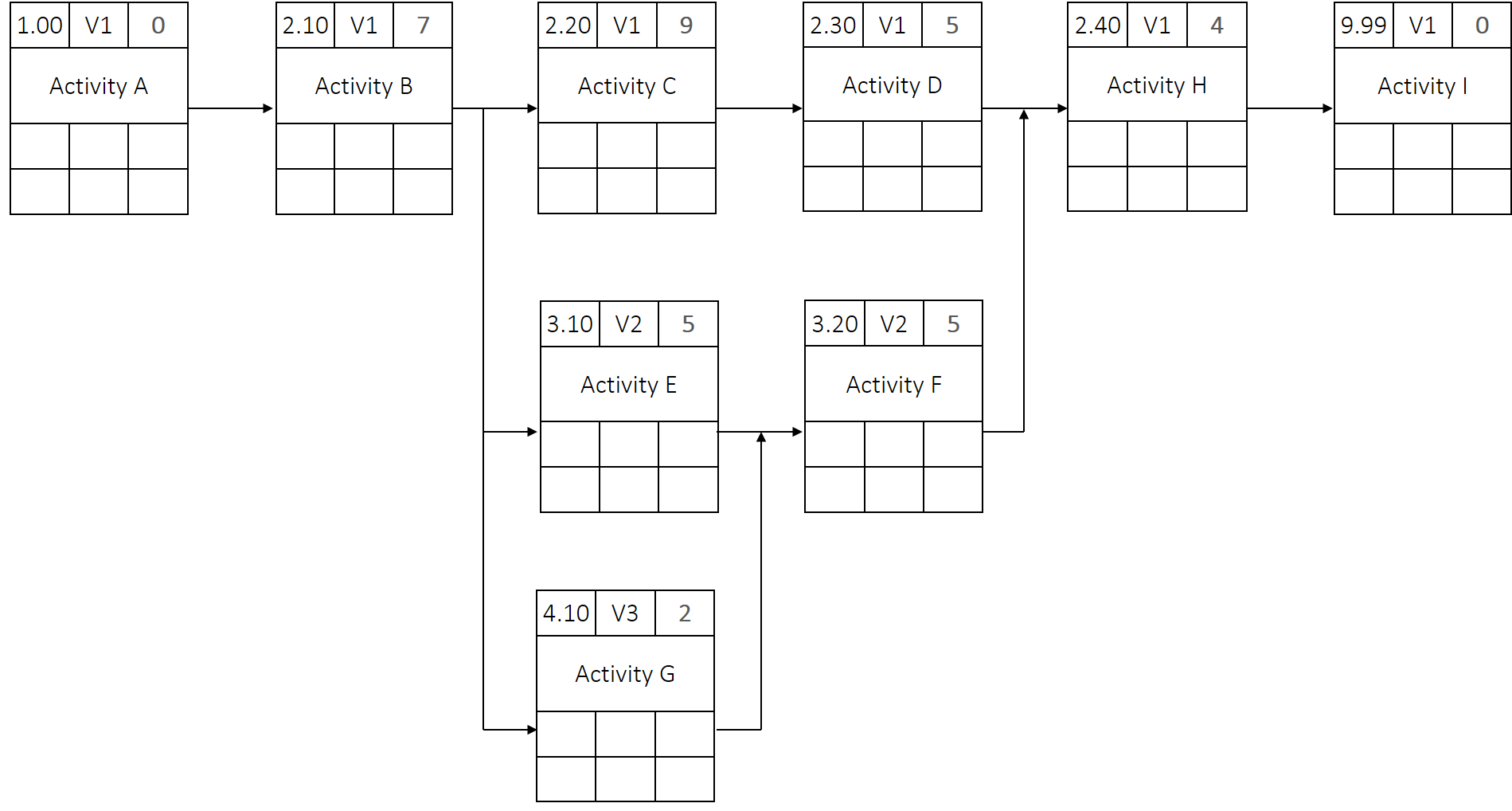
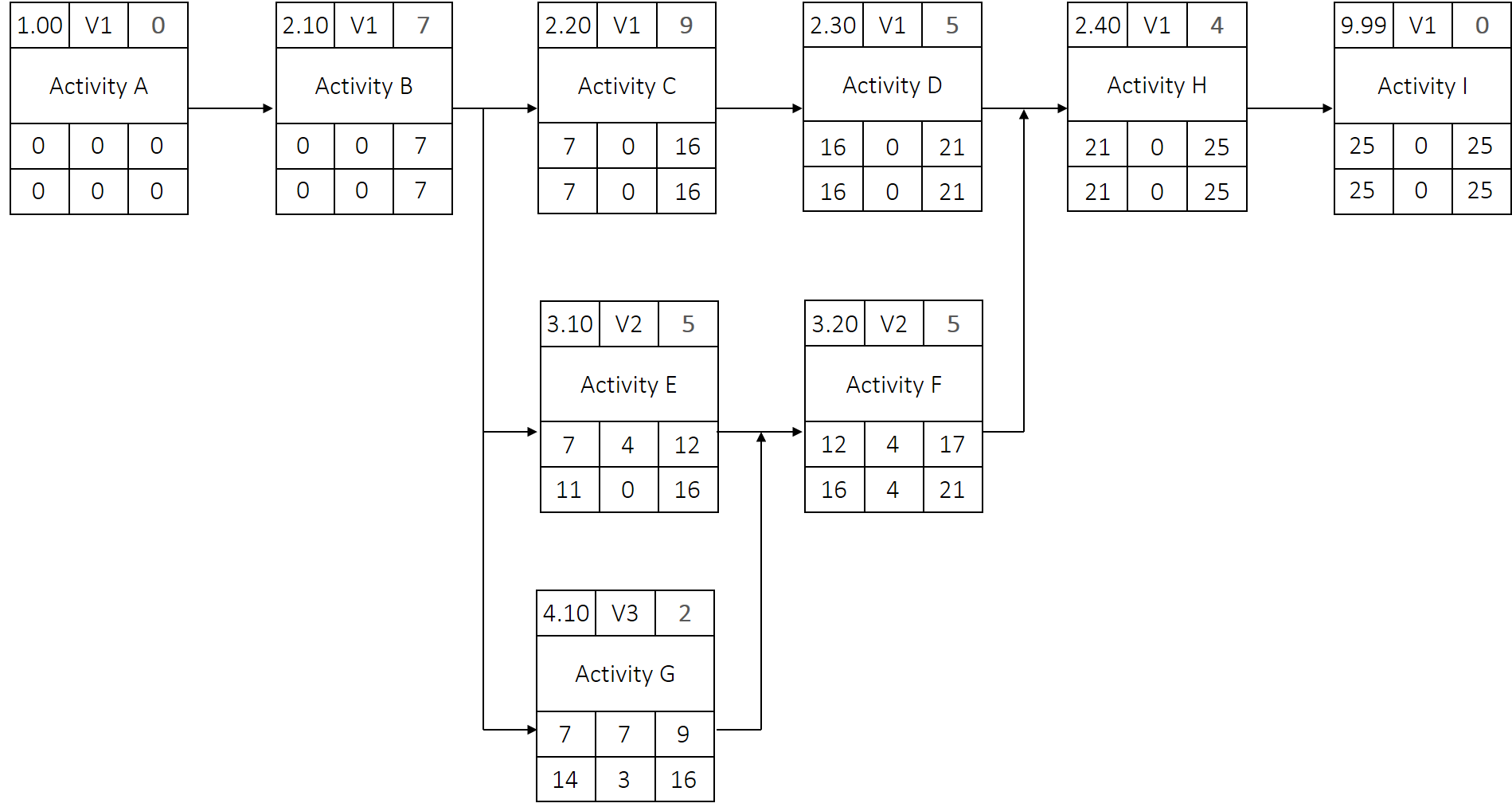
Solution for the second task
How to solve:
Filled out network diagram:
Test yourself!¶
Now it is time to check your knowledge.
Answer the following questions for yourself. Please take your time and think carefully about what you would answer before revealing the solution.
In what order should project time scheduling be realised?
- Specification of work packages
- Definition of processes and creation of a process schedule
- Integration of the process schedule in the time schedule
- Optimisation of the time schedule
- Approval of the project schedule
- Introduction of deadline monitoring
What is a project network diagram?
The network diagram is a a tool for analysis, description, planning and controlling which visualises processes and their interdependencies graphically.
What results do forward-pass and backward-pass calculations deliver for network diagrams?
- Earliest times and deadlines for all events and activities in the network diagram,
- Latest times or deadlines for all events and activities,
- Forward and backward pass calculations are prerequisites for the definition of the critical path and time margins (float).
What types of float exist?
- Total float:
The time between the earliest and latest position of an event or activity (predecessor activity in earliest position and successor activity in latest position) - Free float:
The time by which a predecessor activity can be delayed from its latest position without altering the latest position of other events or activities